Selected Plants of Navajo Rangelands
Take care of our Navajo Rangelands
Plant Types
Plants can be described in various ways. This site separates plants into six types, based on growth form.
Grasses
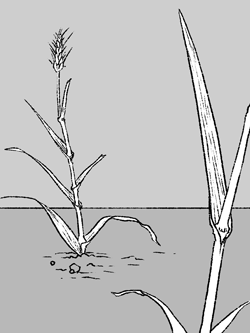
Grasses have a main stem with a sheath and leaves wrapping around
the stem below. Their leaves have parallel veins. Growth
pattern is alternate (leaves staggered on the stem) or basal.
Brush

Also called shrubs, plants in this category are woody and
are usually multi-stemmed and less than 16 feet tall
(with some exceptions). They have shallower roots than
trees.
Vines
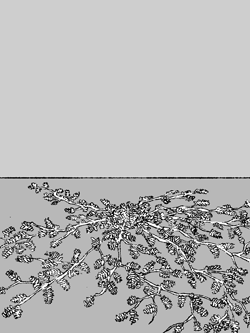
A twining or climbing plant with relatively long stems,
vines grow on something, with tendrils. May have
prominent flowers. Can be woody or herbaceous.
Forbs
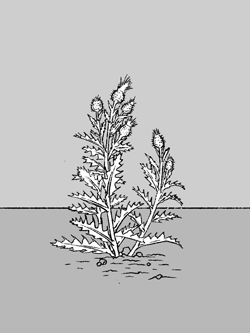
Often called "weeds," forbs usually have a non-woody stem
(easily bent) and prominent flowers. They may be annual,
biennial, or perennial. They can have single or multiple
stems or grow in a basal pattern, meaning all growth comes
from the base.
Cacti
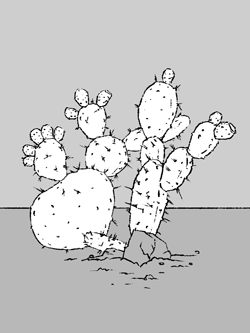
Stems of cacti are thick and succulent, sometimes forming
pads. Leaves are reduced to spines and barbs and grouped
in definite clusters on the stem. Different species have
many differently colored flowers.
Trees
Trees are woody and have bark. They usually have a single
trunk (with some exceptions) and taproots. Different species
have different shapes and kinds of leaves, such as needles,
evergreen leaves, or deciduous leaves.
©2018 NMSU Board of Regents.
Individual photographers retain all rights to their images.
Partially funded by the
Western Sustainable
Agriculture Research and Education Program
(westernsare.org; 435.797.2257),
project EW15-023.
Programs and projects supported by Western SARE are
equally open to all people.